Negombo
Our penultimate stop of the trip - prior to Colombo Airport - was Negombo.
On a more secular level, on our way back to the coast, we stopped at this place for lunch at the café. It was hosting a wedding planning exhibition and in its own way was fascinating - as was the bizarrely incompetent management of the café. Like an episode of 'Fawlty Towers'.

Since we had descended from the highlands, rice had again replaced tea as the predominant crop. It's the staple and almost entirely for domestic consumption. These days it's mechanically harvested and bagged, replacing several steps of back breaking manual labour.
Other important crops include rubber, coconuts, palm oil, bananas, and pineapples, as well as a variety of other fruit and vegetables.
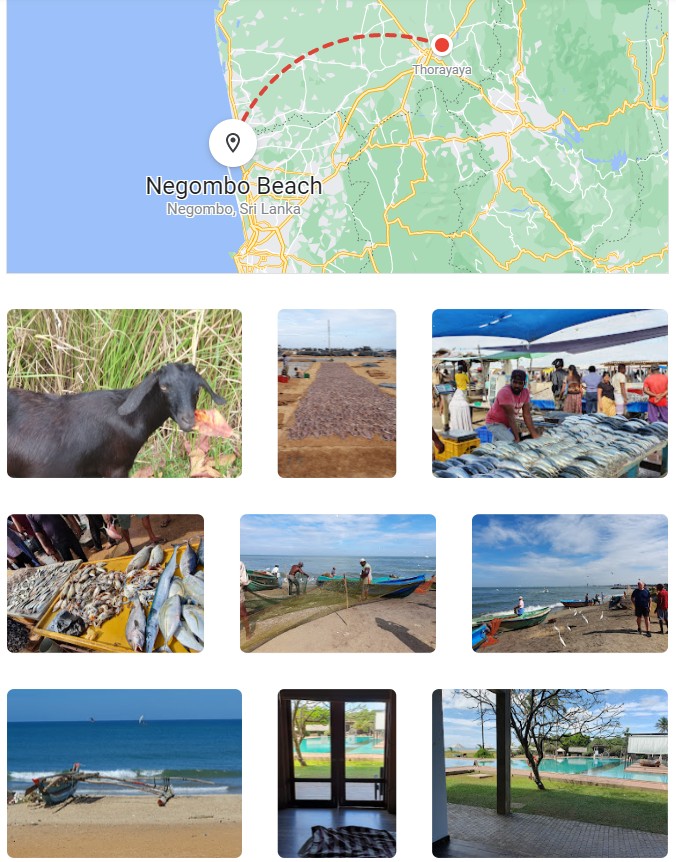
Here we had a visit to the fish markets; walked with goats; and relaxed at the Goldi Sands Hotel (resort).
Time to go home.