(Carbon Sequestration)
Carbon Sequestration Source: Wikimedia Commons
At the present state of technological development in NSW we have few (perhaps no) alternatives to burning coal. But there is a fundamental issue with the proposed underground sequestration of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a means of reducing the impact of coal burning on the atmosphere. This is the same issue that plagues the whole current energy debate. It is the issue of scale.
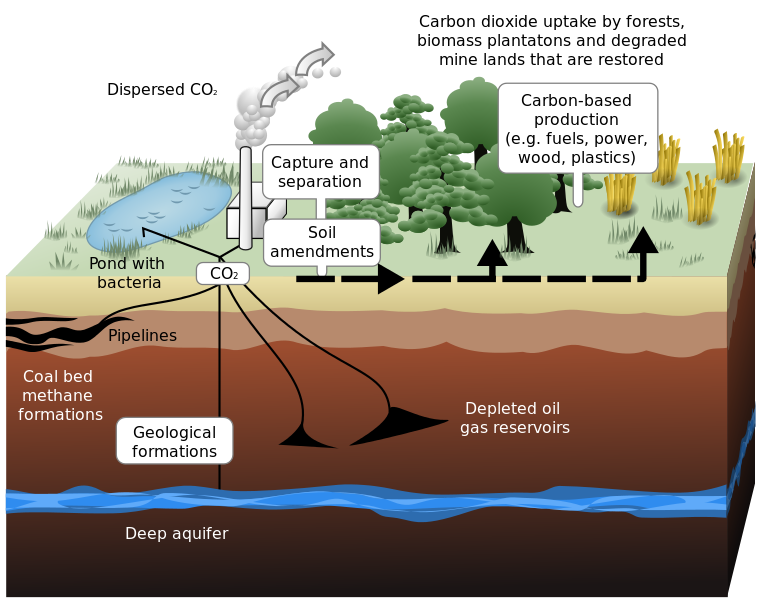
Disposal of liquid CO2: underground; below the seabed; in depleted oil or gas reservoirs; or in deep saline aquifers is technically possible and is already practiced in some oil fields to improve oil extraction. But the scale required for meaningful sequestration of coal sourced carbon dioxide is an enormous engineering and environmental challenge of quite a different magnitude.
It is one thing to land a man on the Moon; it is another to relocate the Great Pyramid (of Cheops) there.
The underground volume required to dispose of coal sourced carbon dioxide is over five times that occupied by the coal that produced it. As discussed in more detail below, to liquify and sequester just 25% of NSW coal sourced CO2 annually (for example that produced by coal fired electricity) would fill a volume of 63 thousand million cubic metres (=251 Km square by 1m deep). As it is expected that this liquid would be pumped into porous strata, where it will fill interstitial voids to perhaps 10% of the volume, several thousand thousand square kilometers of strata would be required annually. These volumes would also require hundreds of kilometres of high pressure distribution pipeline and hundreds of injection bore holes the diameter and depth of oil wells.
Within a few years, the underground sequestration site (or sites) required for CO2 would underlie hundreds of thousands of square kilometres of NSW countryside with high pressure liquid/solid phase CO2 that would pose probably insurmountable: geological; engineering; environmental; aesthetic; safety; and cost issues.
Power generation metals smelting and the mining that supports them are amongst civilisation’s largest enterprises. Present installed coal thermal generating plant capacity in NSW is 12.6 GW. This is the largest electricity generation capacity of any Australian State (32.4% of the total) and bigger than many developed countries including Switzerland, New Zealand and Denmark. But this capacity is dwarfed in world terms. China adds this capacity every few months. A single project, their three gorges dam, will have double our entire capacity. We are small players on the world stage and what we do makes little material difference.
NSW is heavily dependent on coal. In 2005-6 the New South Wales (NSW) coal mining industry produced around 161.3 million tonnes (Mt) of raw coal, yielding 124.7 Mt of saleable coal in 2005-06. This accounted for $8.5 billion in income, or 73% of the total value of the NSW mining sector. Exports of 89.8 Mt of thermal and metallurgical coal totalled approximately $6.7 billion in value, while domestic consumption of 33 Mt of coal by the power, steel and other industries totalled $1.8 billion in value. The remaining saleable coal was placed into mining stocks.[1] Since that time exports have increased and the coal price has more than doubled. Coal is presently worth at least $15 billion a year to the NSW economy, disregarding its economic multipliers.
