Carbon Reduction Imperative
Due to improving living standards in developed and some developing countries (China India, Indonesia, Korea, Malaysia, Vietnam, Singapore etc) the worldwide demand for energy for electricity generation has been growing by around 2% pa worldwide.
Worldwide electrical energy is predominantly based on the combustion of fossil fuels (carbon and a proportion of hydrogen). The carbon is released as atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). The consequent exponential release of CO2is believed to be threatening the climate of the planet. This is compounded by the release of methane and other air, water and land pollution (associated with industrialisation) and the widespread disruption of the natural carbon cycle by tree clearing and broad-acre farming and grazing monocultures and damage to marine ecosystems (as a result of exponential population growth).
In response, carbon mitigation strategies are in place throughout the developed world to attempt to contain the growth of atmospheric CO2. To facilitate these strategies, renewable energy technologies are projected to make an increasing contribution to world energy consumption. The stronger these carbon mitigation strategies are; the more competitive low carbon and renewable energy becomes.
-
Hydro
-
Wind
-
Solar
-
Geothermal
-
Biomass/Biogas (including wood, algae and bio/solar)
-
Marine (tides, waves, currents)
-
Nuclear (including fusion)
Some of these involve more 'whole of life' carbon production in their manufacture; installation; maintenance; demolition; and recycling than others. The following analysis is based on the assumption that they actually run, and produce useful electricity, for their estimated lifetime. If they become ‘white elephants’ their carbon footprint becomes very large indeed.
Comparative Carbon Footprints
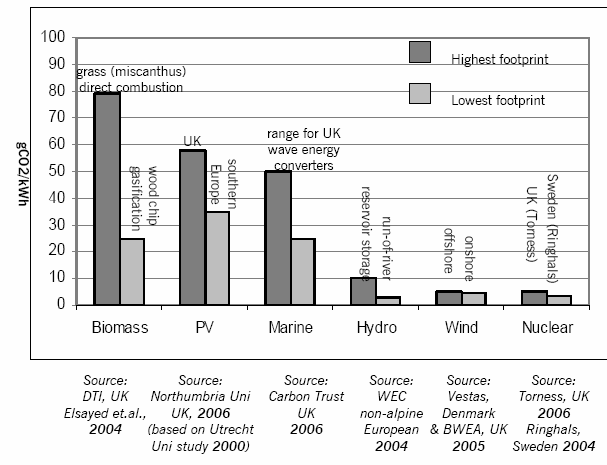
Source: UK Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology - Carbon Footprint of Electricity Generation
